Nakamoto, our AI specialized in cryptocurrency
📅 Published on August 20, 2024
Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin, remains one of the most enigmatic figures of our time. To this day, their identity is still unknown and might remain so.
Nakamoto’s primary motivation was to address the flaws of the banking system, particularly the practice of fractional reserve banking, where banks lend out money they don’t actually possess.
I. Presentation of Nakamoto
In tribute to this vision, we have developed an AI that protects investors from market manipulation, specifically by detecting “pump and dump” schemes aimed at artificially inflating prices.
Bitcoin has indeed attracted significant interest from “whales,” very large traders. In the United States, the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) and FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority) regulate fraud and market manipulation, similar to the AMF (Autorité des marchés financiers) in France.
II. Detection of transactions in the Web3 universe
In the Web3 universe, the detection of transaction holders is done through addresses linked to an electronic wallet. Theoretically, it is impossible to identify the owners of the publicly displayed addresses(2).
III. Features of Nakamoto
We move away from the original philosophy of Bitcoin. In tribute to this philosophy, our AI, named Nakamoto, has analyzed millions of transactions to identify similarities in orders (because it would be too easy if the whales used only one address), in order to detect similar order patterns over several years.
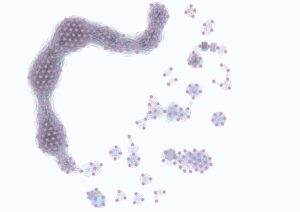
The image illustrates a whale(3) on the left, representing a fraction of addresses that executed exactly the same transaction orders, within a three-second window, analyzed over several years. Pure coincidence, these orders are so significant that they were followed either by a bear market or a bull market. And curiously, these addresses did not make any other orders outside of these massive market movements. Strange, isn’t it?
(1) Bitcoin itself is not directly regulated by these agencies as it is not considered a security but rather a commodity by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). However, any financial product derived from Bitcoin (such as Bitcoin futures) would be under the regulation of the SEC and/or the CFTC. The FINRA regulates brokers and brokerage firms. If these firms offer services related to cryptocurrencies, they must comply with FINRA’s rules. This includes fighting against fraud and market manipulation.
(2) who conduct transactions via DEX (Decentralized Exchange)
(3) It is a graph-based database, with nodes and edges. The edges represent the number of common transactions between the nodes.