Official Documentation – Liris AI Automation Platform
Liris is an artificial intelligence platform designed to automate code generation (Liris Vibe Coding) and the creation of synthetic datasets (Liris Data Science). It excels at providing precise and structurally valid results by using the contextual knowledge of existing projects.
Quick Start 3 Steps
Upload your project or access existing configurations. Liris analyzes the structure and builds the relationship graph.
Write a natural language prompt describing the code to be generated (Liris Vibe Coding) or the dataset to be created (Liris Data Science).
Liris uses the project context (code or dataset) to generate a relevant response and displays it in the snippet.
Global Liris Architecture
The Liris system is built around three main pillars that ensure seamless integration between your workspace and advanced language models (LLMs):
- Ingestion and Modeling: The construction phase of the Knowledge Graph.
- Automation Engine: Management of the Dynamic Prompt and Automatic Navigation.
- User Interface: The extension (VS Code) and control panel for configuration and output management (Snippet).
Figure 1 – The three pillars of Liris architecture. 
Installation and Login
To get started, integrating Liris into your development environment involves a few simple steps:
-Extension Installation
Liris is primarily used via a VS Code extension, which allows for native integration of generated code into your IDE.
-Access Configuration (API)
Connection to AI models is managed in the Configuration tab of the Liris platform. You must insert your access keys for external LLM providers (OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.) there.
Figure 2 – Interface for configuring API keys for LLMs.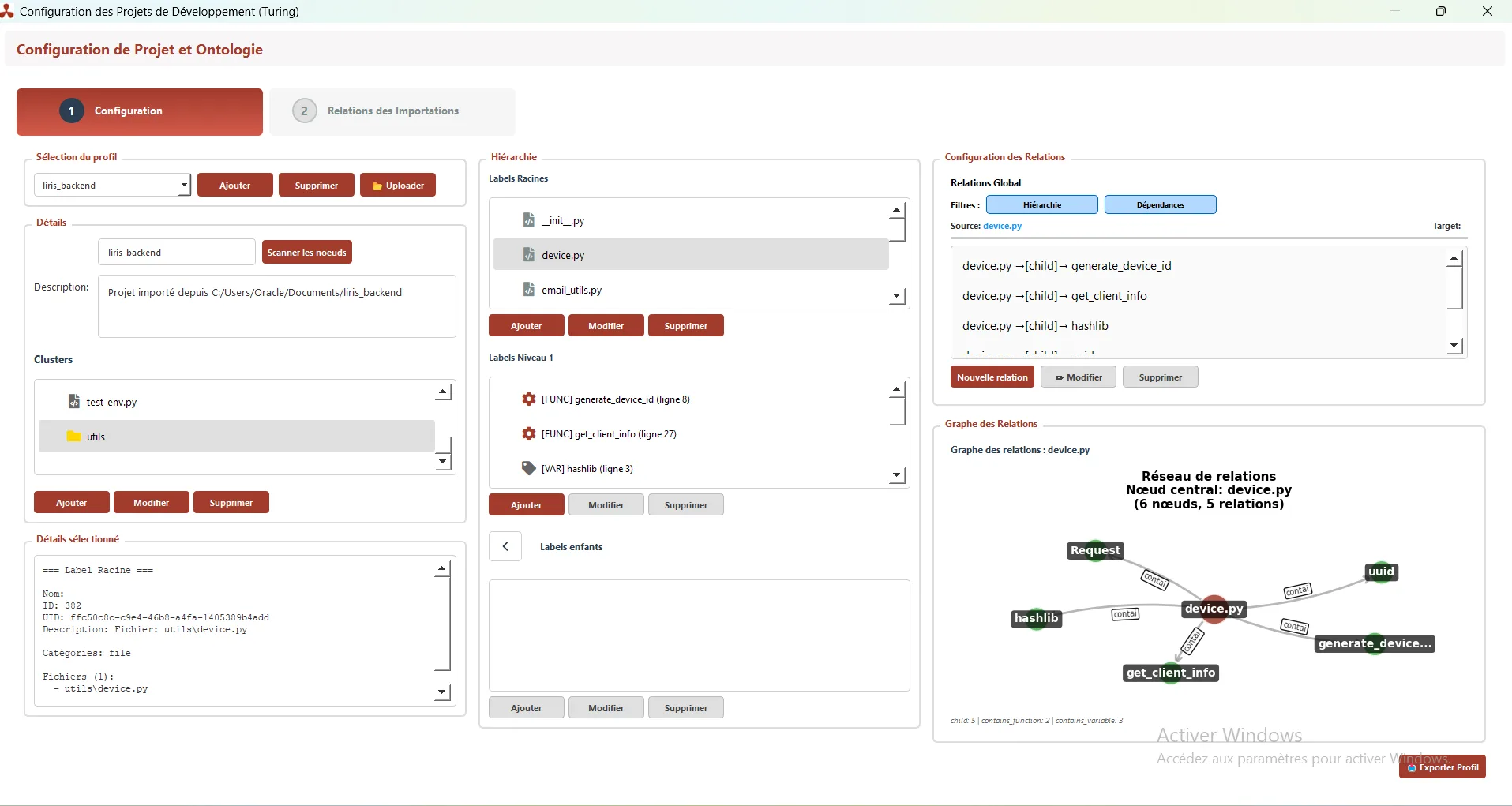
Knowledge Graph: The Brain of Liris
The Knowledge Graph is the semantic and structural representation of your project. It is generated immediately after the Upload action of a directory or the configuration of a dataset.
-Graph Construction
The static and dynamic analysis process breaks the project down into:
- Nodes (Entities): Files, Classes, Functions/Methods, Data Typologies.
- Relationships (Edges): Logical and functional links between nodes. These relationships are key to understanding context:
- Inheritance: ‘inherits from’ relationships between classes.
- Dependency: ‘calls’ or ‘uses’ relationships for a method or function.
- Structuring: ‘contains’ relationships for an attribute or variable.
Figure 3 – Graphical representation of complex relationships within the Knowledge Graph. 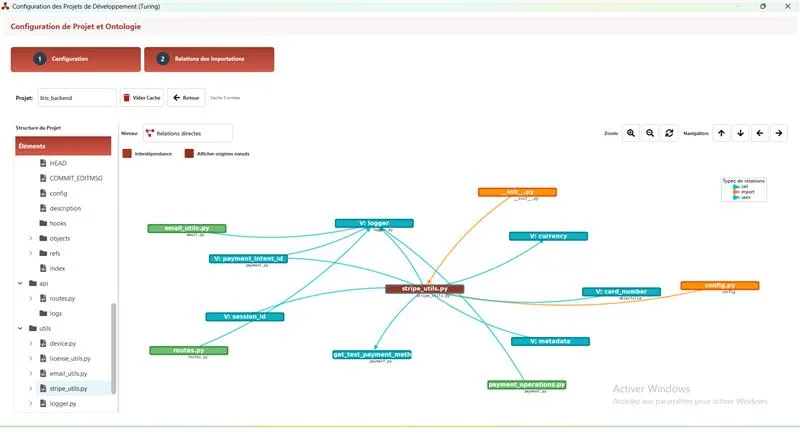
-Role in Generation
The Graph allows providing LLMs with precise and complete context, even for large projects, by avoiding sending the entire code. This ensures:
- Structural Validity: The generated code respects existing interfaces and signatures.
- Relevance: Only necessary information is included in the prompt, optimizing LLM efficiency.
Prompting Engine (Dynamic Prompt)
The Prompting Engine is the Liris algorithm that transforms the user request into a highly optimized instruction for the AI.
-Triggering and Context
After writing your request in the Coding interface:
Figure 4 – Writing the initial request (Prompt) in the Liris interface. 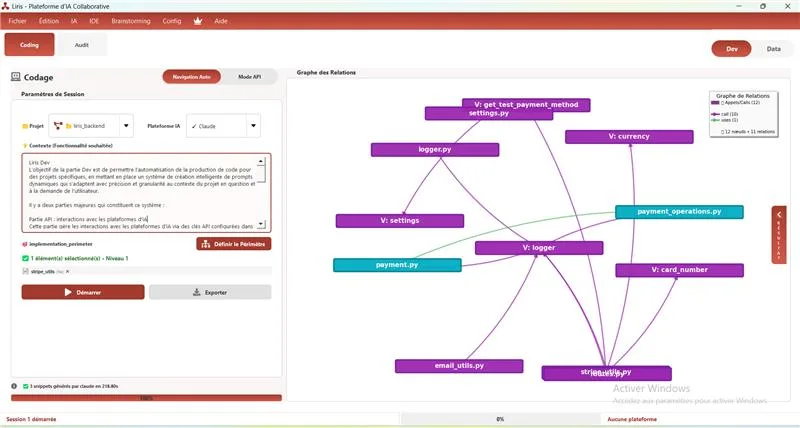
The algorithm analyzes the prompt to identify target entities. It then uses the Knowledge Graph to dynamically extract associated code fragments or data schemas.
-Final Prompt Composition
The Final Prompt sent to the LLM is an intelligent combination of:
- The user’s initial request.
- Full definitions of the mentioned entities.
- Direct and indirect contextual relationships (dependencies).
The Snippet (Output and Integration)
The Snippet is the area of the Liris interface that serves as the final control and validation point for AI-generated results.
-Single Collection Point
Regardless of the generation method (API or Automatic Navigation), the code or dataset is always displayed in the Snippet for:
- Review: The user checks the validity and accuracy of the result.
- Validation: Confirms generation before integration.
Figure 5 – The Snippet displaying the generated code or dataset, ready for integration. 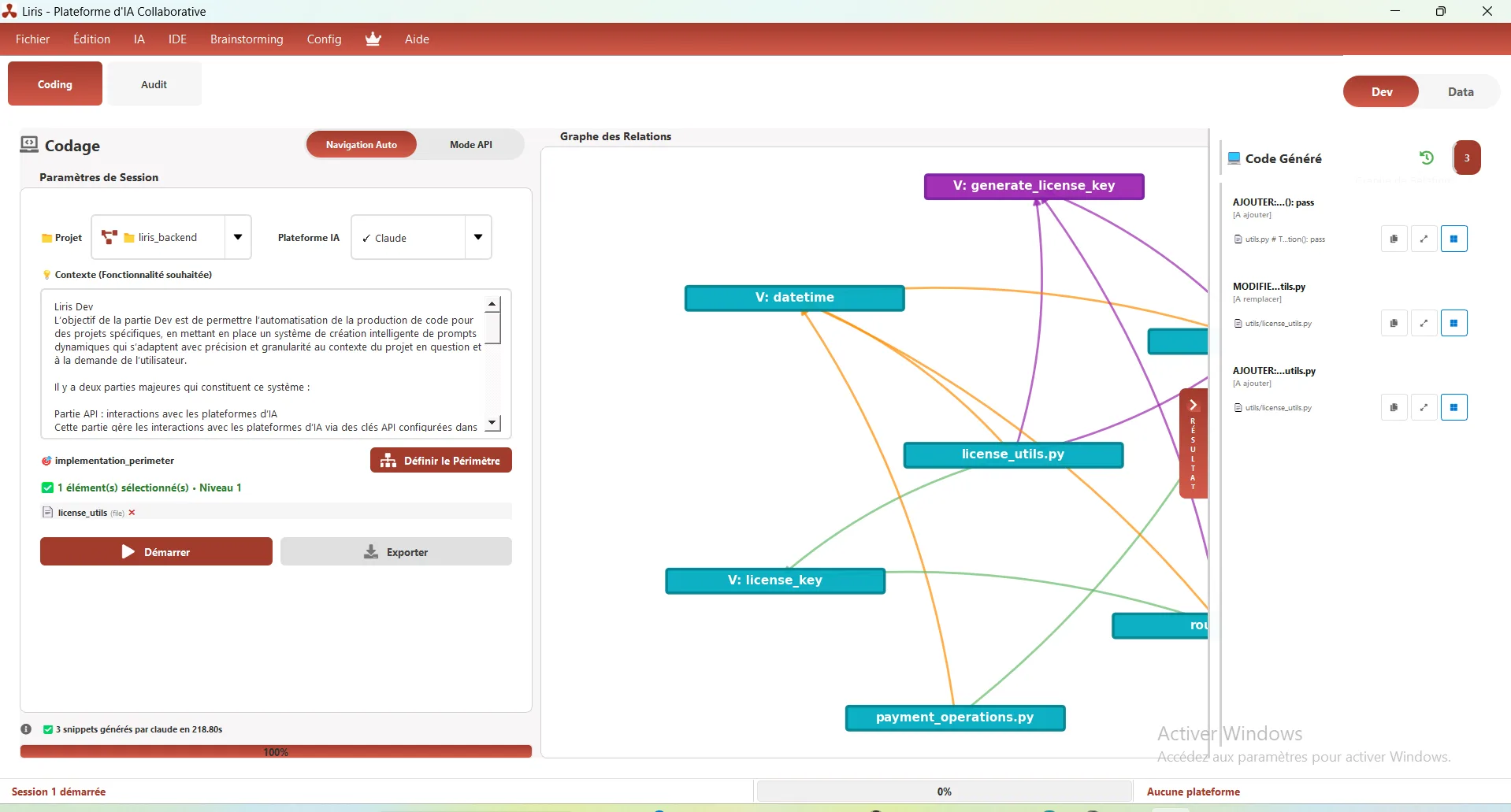
-Final Integration
From the Snippet:
- Liris Vibe Coding: The code is directly integrated into the IDE (via the VS Code extension) at the correct location in the project structure.
- Liris Data Science: The dataset can be downloaded in the desired format (JSON, CSV).
Liris Vibe Coding
Objective
Automate code production via a dynamic prompt system adaptable to project context and user demand. Focus on code generation and integration.
System Components
API Integration
Manages AI interactions via API keys. Automates prompt sending and response extraction.
API Process
Retrieves context, sends AI prompt, displays generated code in the snippet.
Automation Engine
Automates AI interactions. Controls computer (mouse/keyboard), navigates to AI, enters and validates prompt, detects response completion via CSS, retrieves and displays response.
Integration Layer
Inserts results into the snippet. VS Code extension bridges IDE and Liris.
Context Processing
Configures and saves context in graph database. Optimized ontology with hierarchical decomposition (clusters, root labels, parents, children). Pydgraph mutations insert clusters/labels.
Contextual Engineering
Structural Memory via Turing Graph
Complete structural project memory through graph database for precise context awareness.
High-Fidelity Prompt Generation
Generates high-fidelity prompts using graph context for accurate code generation.
Total Resilience with Dual Mode
Dual mode operation (API & automation) ensures compatibility with any AI platform.
Intelligent CSS Selector Extraction
Intelligent extraction via CSS selectors for precise response retrieval.
Key Components
Knowledge Graph
Complete project representation with nodes and relationships.
Prompting Engine
Dynamic prompt generation system with graph context adaptation.
Automatic Navigation
Browser automation for AI interface compatibility.
Snippet
Single display point for final results with validation and integration.
Final Integration
Seamless code integration into IDE via VS Code extension.
VS Code Extension
Extension bridging Liris application and development environment.
Liris Data Science
Objective
Generate realistic synthetic datasets. Configure contextual parameters, adapt data formatting, and provide statistical visualization of context combinations used.
User Journey for Dataset Generation
Define Strategy
In the Dataset Strategy tab, create and configure different context typologies.
Structure Taxonomy
For taxonomic contexts, define hierarchical structure (cluster > root label > parent > child).
Configure Generation
In the Dataset Generation tab, compose prompt with selected contexts, choose AI platform, output format, and number of batches.
Launch Generation
Click Generate to start the process.
Tab Descriptions
1. Dataset Strategy
Objective Define context typologies for a project.
Components
- Pie Chart Diagram showing context combination distribution
- Context Typology Management Add/modify/save hierarchical structures (cluster > root label > parent > child)
2. Dataset Generation
Objective Merge context typologies, send to AI, and retrieve result in a file.
Components
- Typology Combination Establish context combinations to generate batches
- Progress Visualization Visual indicator to track process status
- Prompt Editor Text area to compose prompt to send with context typologies
- Dataset Template Selection of predefined data formatting models
- Output Format Selection of final file format (CSV, JSON)
Liris Data Science Key Features
Custom Dataset Architect
Ability to create massive, ultra-specific datasets from purely theoretical scenarios.
Hierarchical Business Taxonomy
Enforce structure (Cluster > Label > Parent > Child) for AI generation, creating organized business taxonomies.
Statistical Steering
Visual tool (representativity pie chart) that analyzes generation strategy before launch, showing context combination distribution.
Industrial Batch Generation
Configuration allowing mixing of complex context combinations and producing them in series via batch processing.
Multi-Format Augmentation and Formatting Engine
Manages final formatting (CSV, JSON) via templates and can “augment” data from existing examples.
Dataset Configuration
Typologies
Definition of different context typologies to structure data according to business needs.
Combinations
Configuration of possible combinations between different typologies to create varied datasets.
Generation and Validation
Dynamic Prompt
Dynamic prompts that automatically adapt to selected contexts for optimal generation.
Distribution Visualization
Statistical visualization of context combinations used to analyze data distribution.
Dataset Download
Download of generated dataset in JSON/CSV formats according to usage needs.